1 前言
总结一下,最近老师上课讲的排序算法……毕竟上课没认真听,就得自己花点时间了…..
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/dongfei2033/article/details/79938651
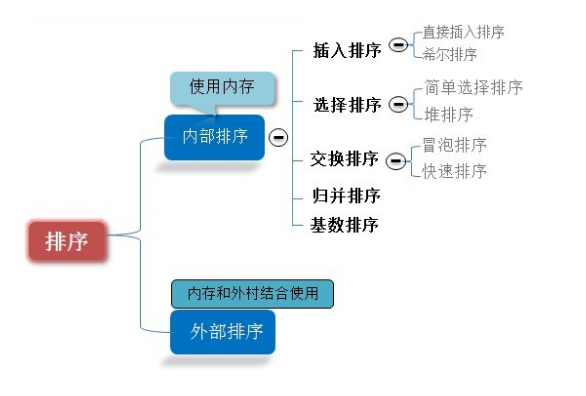
2 排序算法
2.1 冒泡排序
2.1.1 数组实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| void bublletSort(int a[],int len)
{
int temp;
for(int i=0;i<len-1;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<len-i;j++)
{
if(a[j]>a[j+1])
{
temp = a[j];
a[j] = a[j+1];
a[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
|
2.1.2 链表实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
| #include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include<typeinfo>
using namespace std;
#define END_CODE -999
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct lnode {
ElemType data;
struct lnode *next;
} LNode;
void show(LNode *L);
LNode *create_LinkList_H( ) {
LNode *head, *q;
head = new LNode;
head->next = NULL;
ElemType data;
cout<<"input data : "<<END_CODE<<" to stop!\n";
while( true ) {
cin >> data;
if( data == END_CODE ) {
break;
}
q = new LNode;
q->data = data;
q->next = head->next;
head->next = q;
cout << "Node" << q->data << "create successfully!\n";
}
return (head);
}
void BubbletSort(LNode *head)
{
LNode *p,*q;
int s;
for(p=head->next;p!=NULL;p=p->next)
for(q=p->next;q!=NULL;q=q->next)
if((p->data)>(q->data))
{
s=p->data;
p->data = q->data;
q->data = s;
}
}
void show(LNode *L) {
if(L->next == NULL) {
cout << "linklist: empty!!!\n";
return;
}
LNode *q = L->next;
cout << "number: ";
while(q != NULL) {
cout << " " << q->data;
q = q->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
LNode *head = create_LinkList_H();
show(head);
BubbletSort(head);
show(head);
return 0;
}
|
2.2 插入排序
2.2.1 数组实现
原理参考链接:直接插入排序(数组实现)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| #include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
void insertSort(int a[],int n)
{
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
int key=a[i];
int j=i-1;
while(j>=0&&a[j]>key)
{
a[j+1] = a[j];
j--;
}
a[j+1] = key;
}
}
int main()
{
int a[] = { 2,1,4,5,3,8,7,9,0,6 };
int n=10;
insertSort(a,n);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
|
2.2.2 链表实现
主要思想和使用数组实现是一个道理,但是感觉比数组要不好理解一点
代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
| #include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include<typeinfo>
using namespace std;
#define END_CODE -999
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct lnode {
ElemType data;
struct lnode *next;
} LNode;
void show(LNode *L);
LNode *create_LinkList_H( ) {
LNode *head, *q;
head = new LNode;
head->next = NULL;
ElemType data;
cout<<"input data : "<<END_CODE<<" to stop!\n";
while( true ) {
cin >> data;
if( data == END_CODE ) {
break;
}
q = new LNode;
q->data = data;
q->next = head->next;
head->next = q;
cout << "Node" << q->data << "create successfully!\n";
}
return (head);
}
void InsertSort(LNode *L){
LNode *p,*r,*q;
p=L->next;
q=p->next;
p->next=NULL;
p=q;
while(p!=NULL){
q=p->next;
r=L;
while(r->next!=NULL&&r->next->data<p->data){
r=r->next;
}
p->next = r->next;
r->next = p;
p=q;
}
}
void show(LNode *L) {
if(L->next == NULL) {
cout << "linklist: empty!!!\n";
return;
}
LNode *q = L->next;
cout << "number: ";
while(q != NULL) {
cout << " " << q->data;
q = q->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
LNode *head = create_LinkList_H();
show(head);
InsertSort(head);
show(head);
return 0;
}
|
2.3 选择排序
2.3.1 数组实现
原理参考:选择排序(数组实现)
实际上选择排序是冒泡排序的升级版…..
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| void selectSort(int a[],int len)
{
int minindex,temp;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
minindex=i;
for(int j=i+1;j<len;j++)
{
if(a[j]<a[minindex]) minindex=j;
}
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[minindex];
a[minindex] = temp;
}
}
|
2.3.2 链表实现
待补充……
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
| #include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include<typeinfo>
using namespace std;
#define END_CODE -999
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct lnode {
ElemType data;
struct lnode *next;
} LNode,*LinkList;
void show(LNode *L);
LNode *create_LinkList_H( ) {
LNode *head, *q;
head = new LNode;
head->next = NULL;
ElemType data;
cout<<"input data : "<<END_CODE<<" to stop!\n";
while( true ) {
cin >> data;
if( data == END_CODE ) {
break;
}
q = new LNode;
q->data = data;
q->next = head->next;
head->next = q;
cout << "Node" << q->data << "create successfully!\n";
}
return (head);
}
void SelectSort(LinkList &L)
{
LinkList p = L->next;
LinkList minindex;
LinkList q;
int temp;
while(p)
{
q=p->next;
minindex=p;
while(q)
{
if(q->data<minindex->data) minindex=q;
q=q->next;
if(minindex!=p)
{
temp = minindex->data;
minindex->data = p->data;
p->data = temp;
}
}
p=p->next;
}
}
void show(LNode *L) {
if(L->next == NULL) {
cout << "linklist: empty!!!\n";
return;
}
LNode *q = L->next;
cout << "number: ";
while(q != NULL) {
cout << " " << q->data;
q = q->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
LNode *head = create_LinkList_H();
show(head);
SelectSort(head);
show(head);
return 0;
}
|
2.4 快速排序
2.4.1 数组实现
原理参考:快速排序原理
代码参考如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| #include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
void quickSort(int a[],int left,int right)
{
int i,j,t,temp;
if(left>=right)
return;
temp=a[left];
i=left;
j=right;
while(i!=j)
{
while(a[j]>=temp&&i<j) j--;
while(a[i]<=temp&&i<j) i++;
if(i<j)
{
t=a[i];
a[i]=a[j];
a[j]=t;
}
}
a[left]=a[i];
a[i]=temp;
quickSort(a,left,i-1);
quickSort(a,i+1,right);
}
int main()
{
int a[] = { 3,1,4,5,2,8,7,9,6,0 };
int n=10;
quickSort(a,0,9);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
|
